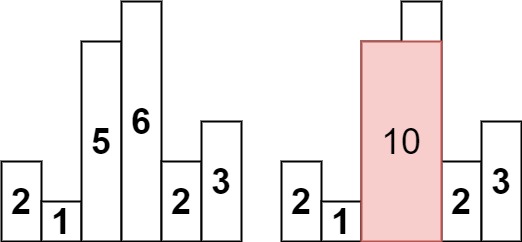
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10

The next smaller element to the right and the next smaller element to the left. The width of the rectangle is (right-left-1) if the NSE to the right and the NSE to the left.
package pep.Day26;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Largest_Area_Histogram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3};
// this will start from right
int[] nextSmallerToLeft = nextSmallerToLeft(arr);
display(nextSmallerToLeft);
// this will start from left
int[] nextSmallerToRight = nextSmallerToRight(arr);
display(nextSmallerToRight);
int maxArea = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nextSmallerToLeft.length; i++) {
int length = (nextSmallerToRight[i] - nextSmallerToLeft[i] - 1);
int area = length * arr[i];
maxArea = (int) Math.max(area, maxArea);
}
System.out.println(maxArea);
}
private static int[] nextSmallerToLeft(int[] arr) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = arr.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[i] <= arr[stack.peek()]) stack.pop();
// if smaller to right not found, insert in ans -1
ans[i] = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
private static void display(int[] ans1) {
for (int x : ans1)
System.out.print(x + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
private static int[] nextSmallerToRight(int[] arr) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = arr.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[i] <= arr[stack.peek()]) stack.pop();
// if smaller to left not found, insert in ans size_of_array
ans[i] = stack.isEmpty() ? n : stack.peek();
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}

No comments:
Post a Comment